Creating RAID(s) in Ubuntu Server 12.04 Installer
After you have all the partitioning done, it’s time to create your RAID(s). This tutorial shows how to create two separate arrays: one for the /boot partition and one for everything else. Since we’re using LVM, it’s possible to use only one array. It’s only required to have a separate array if you are using LVM inside of LUKS containers — which we aren’t.
From the main partitioning screen (as shown above), select “Configure software RAID.”
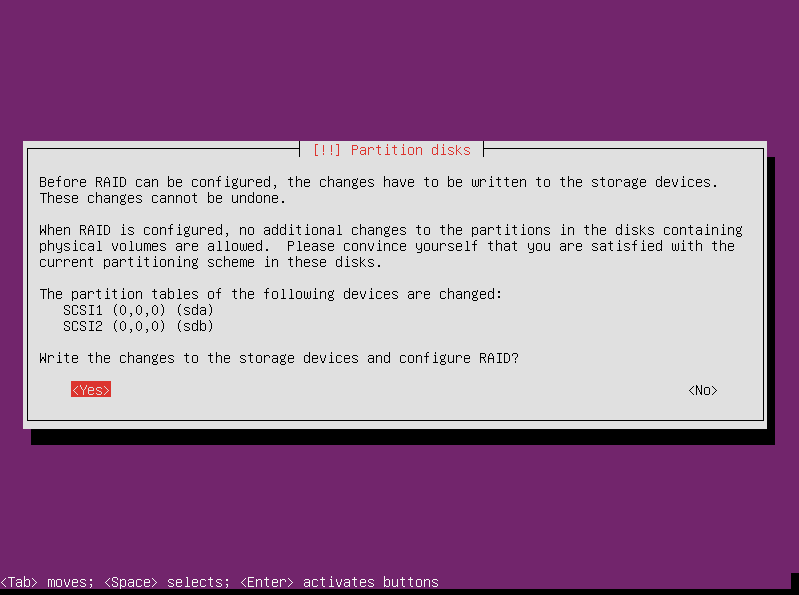
You can’t change the partitions after RAID is configured, so the partitioner wants to confirm that you are satisfied with the changes you have made to the disk partitions. If so, select yes.
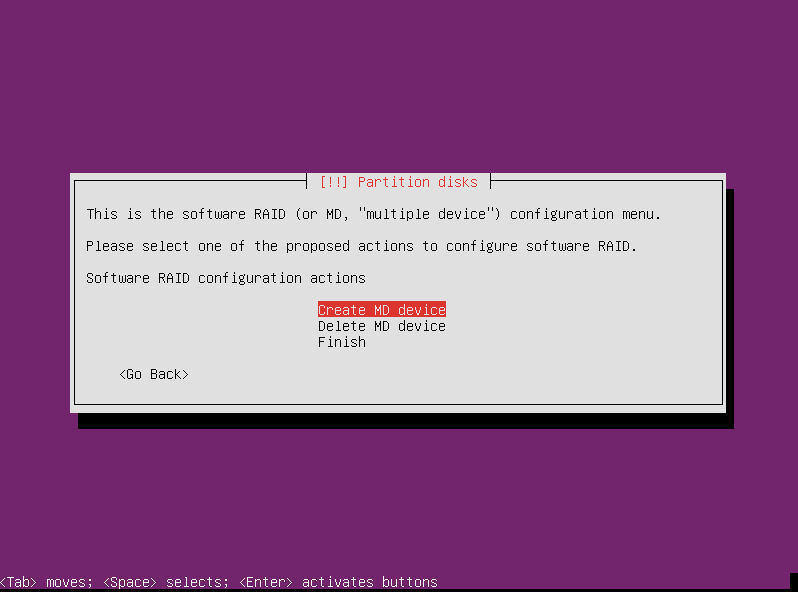
On the next screen select “Create MD device.”

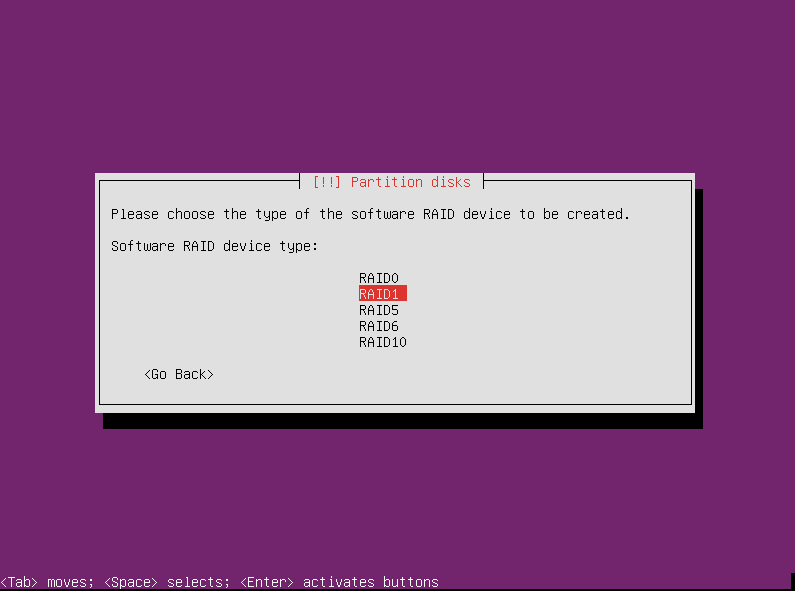
Here you select what type of RAID you want to configure. In this tutorial, we are only using two drives so we can only practically use a RAID0 or RAID1. (If you are doing a setup with more devices, you can setup a different kind of RAID following the same principles shown in this tutorial.)
RAID0 doesn’t offer any redundancy, and therefore no data protection in case of a drive failure, so that’s a bad option for our purposes. Select RAID1 and press enter to continue.
Enter how many active devices you want in the array. We only have two in this computer, so the installer defaults to two.
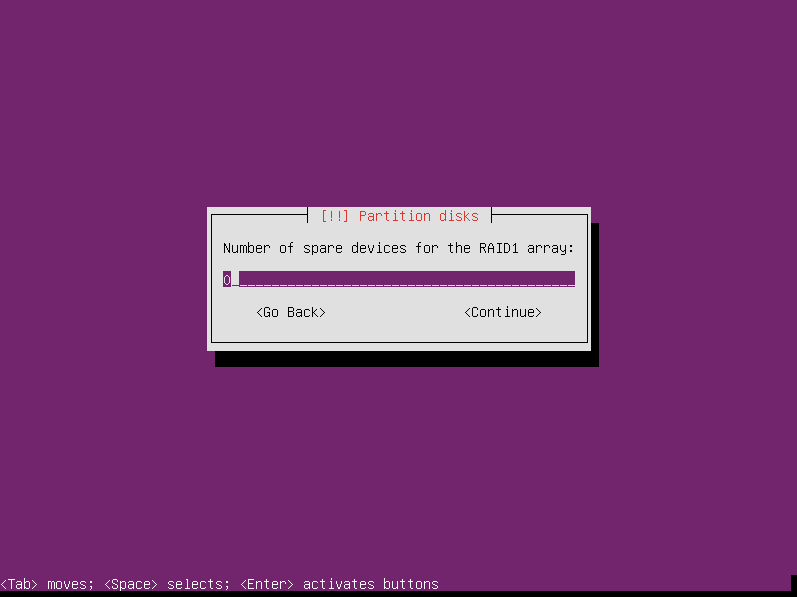
Next you enter how many spare devices you want in the array. Again, we only have two devices in this computer, so we have to leave it at 0. If you have more drives available you can keep some as spares. Then when a drive dies, a spare can quickly be activated to replace it.
The next screen asks you which devices to put in this array. It doesn’t matter if you choose to make your /boot array first or second. For this tutorial, I made it first.

You are then returned to the MD creation menu. Since we now have one MD device already created, you have the additional option to delete an MD device. This is useful if you made a mistake. Otherwise, follow the same steps to create the other array. After you’re done, select “Finish.”
Now with the new installers the bootable flag cannot be set to on for the raid partitions which means you cannot configure raid 🙁 Moreover the boot now is by default set to EFIboot which complicates things even better. The combination of raid 1 and lvm is critical for professional environments. This is a great tutorial. Could you update it? That would be awesome. Thanks!
I’m not sure what you mean by “the new installers.”
he means the installers from 14.04 – these changed many things…
Thank you — this was extremely helpful!!
Hey, Jonathan! Glad to hear it helped.
Great tutorial. Thanks for taking the time to do this.
Thanks, Gary. Glad to help.
I am having a problem with this setup. If I unplug either drive, the system will not boot. I get the error message: “Begin: Waiting for encrypted source device……”. So far I have not been able to find any help on what the solution to this is.
Thank you,
Gary
The instructions here are very clear and helpful. BUT I built it with Ubuntu Server 14.04.1 and have the same problem as Gary – if I unplug either drive and boot, the system says “no volume groups found … waiting for encrypted source device”
I then rebuilt with RAID->LUKS->LVM rather than RAID->LVM->LUKS but get exactly the same problem.
Lst time I tried this (in 2010) the same problem cropped up. I really don’t think Ubuntu has paid much attention to the need for encrypted RAID to work.
I even tried putting a clean disk in place of the “removed” disk to see if it rebuilt, but still says just “waiting for encrypted source device”.
I gave up on Ubuntu for this. Instead I installed a minimal version of Debian 6.0.10 and the encrypted RAID works perfectly; that is removing either drive still allows you to enter your passphrase and log in.
Seems to me there is no point using Ubuntu for encryption with RAID if you can’t boot when a drive fails. And since I am about to build a HP microserver for file storage, I do not want to get burnt by a buggy RAID/Encryption setup.
Thanks “the new guy” for the detailed instructions though, they are probably applicable to Debian and maybe other OS’s too.
Hi The New Guy.
I also have “The new installer”, downloaded today and the bugs that George Pligor speaks of are also preventing me from being able to configure a software RAID 1 array on Ubuntu 12.04.3 LTS 64-bit Server.
Some of the changes include:
Not being given a choice to make a partition Primary or Logical.
An added line to give a partition a name
The inability to set the Bootable Flag to “on”.
The bootable flag of course is the killer. It means grub will not instal.
I am unsure why they changed the installer, but I really wish they hadn’t.
I would really like to get my hands on the old installer because the new installer doesn’t recognize a hardware RAID1 array setup in the Intel RAID Utility on my Gigabyte Z87M-D3HP Motherboard either.
OK, so there is no such thing as a “new installer”
turns out the problem was that I was using 3TB HDDs. anything bigger the 2TB and the Partition table needs to be forced to GPT.
The current installer is not able to cope with rives larger than 2TB for RAID.
You need to set the partitions up first in something like GParted (I used GParted Live CD, or you can use Ubuntu Desktop Live DVD and use its GParted.)
explicitly set the Partition table to GPT.
create a partition at least 1.0MB with no file system and set its flag “biosgrub”
create your swap partition and set its flag “raid”
create your main partition and set its flag “raid”
repeat for the other HDD
exit and begin normal instal.
Once you get to the Partitioner, the partitions are already setup, just do the RAID Configuration.
Create MD swap
create MD main
back in the partitioner, choose swap in the array and choose “use as” – swap area
choose the main in the array and choose “use as” – ext4 – mount – / (root)
DONE.
not need to worry about setting bootable flag.
Finish and write changes to disk.
Install will then work.
This is only for HDDs above 2TB that this is necessary.
solution found here:
http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=2109438
Thanks for your input, Alan. Those bigger drives pose some interesting challenges.
I read this 2 years later and it’s going to save my day! I had no idea the 2GB limit was a problem, took me forever to start searching and here, of all places my search hits sent me to, at last I find a decent explanation…
Thx a zillion!
This guide was great – thanks for taking the time to prepare!
Hi The New Guy,
Thanks for the effort , the tutorial is clear and very helpful.
I have a question, need advise / help.
With the same setup like the example with a RAID 1 with 2 drives setup , if one of drive is dead and what steps to recover the array after a brand new unformatted hard drive is replaced .
Good documentation like this is priceless thank you for taking the time to write it 🙂 I am interested in Ubuntu administration and will be following this site for future entries
There be any problems with an encrypted partition by adding another PV in LVM? Could you describe the process more?
1) Create new PV (only one drive without MD for simplify): pvcreate /dev/sdc
2) Add PV to VG: vgextend linus /dev/sdc
3) Extend LV: lvextend -LXXX /dev/linus/root
4) Anything with /dev/maper/linux-root_crypt??
5) Resize fs: resize2fs /dev/maper/linux-root_crypt
4) cryptsetup resize…
🙂
Thank You!
This is extremely helpful and easy to follow!
Is not /home missing in this tutorial or is it created automatically within / ?
Awesome tutorial! Thanks a lot!